All basics you need to know about screws
13239 Views |

All basics you need to know about screws
Hello everyone! My name is Kazuki Sugimoto from sales department, Hanshin Neji Co.,Ltd.
It’s already April, I think this period is a welcoming time for new workforce, some of you may entered fasteners industry for the first time and still very new to this industry. You may have a lot of question about fasteners. Today, I will help you to clarify basic things about fasteners.
Today, I would like to introduce you to the basics of screws so that you can get even a little interested in screws industry, so please watch this video as below until the end.
This video is about strength classification of screws (Sorry, only it was in Japanese)
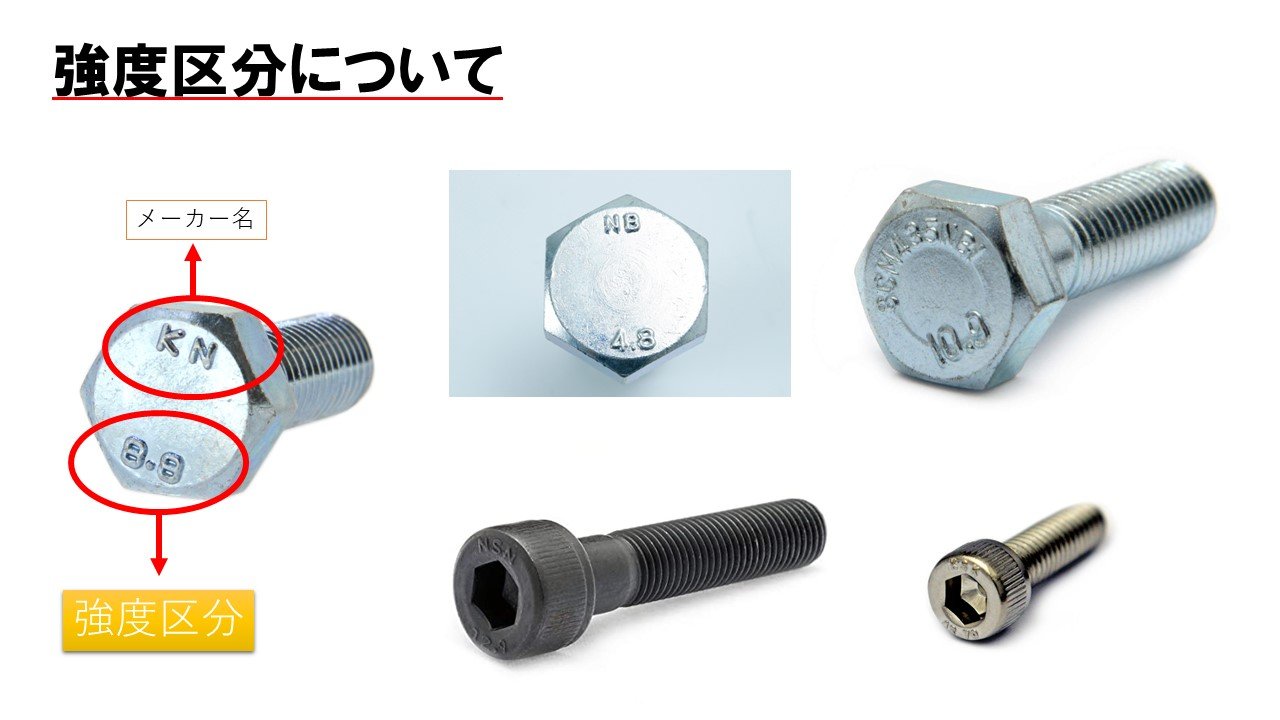
Firstly, I would like to explain the strength classification of screws.

First number on the left represents the tensile strength. For example, in Figure 1, it says 10, but if you multiply it by 100, it has a tensile strength of 1,000N/㎟, this screws can withstand tensile strength up to 1,000N/㎟
In other word, if a force of 1,000N or more is fastened to the screw, the bolt will break as shown in Figure 2.
The number "9" on the right side represents the yield point, and the screw can return to its original state even if it is pulled with a force of up to 90% of 1,000N/㎟
Imagine screw is rubber, when you pulled it, it also wanting to return itself into original state
A screw is be able to mount an object by being pulled and returning itself to original state. If it's up to 90%, it'll be back to normal. On the other hand, if you go further than that, the material will stretch to the point that it can’t return to its original state, this called “permanent deformation”
For example, 8.8 bolt can withstand tensile strength up to 800N/㎟
8.8 means that if a 80% force of 800N (640N) is applied, the screw is be able to its original position, but if more force is applied, it will become completely stretched. In other words, it lose it’s ability to work as screw, and it will become loose or broke.
Baking process
As I mentioned about high-strength fasteners earlier, as Electro galvanized(One type of Plating) high-strength fasteners need baking process to get rid of remaining Hydrogen to prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement. If there is no baking, bolt will have a high possibility to be broken. For baking, it needed 200 C° for 8 – 24 hours to completely remove the hydrogen from material.
Baking treatment is needed for high strength bolts of 8.8 and 10.9 with Electro galvanized.
There are many cases of 12.9 Zinc plated screw that became broke after fastened, so please be careful about this.
Mill sheet
Mill sheet is a document that represent to material information which is used for making fastener, so this document will be issued by material manufacturer company. It is containing chemical properties, manufacture date, lot number, testing data and etc.
So, if you need mill sheet document, please inform to the fasteners company you are going to purchase fasteners in advance because product lot no. is needed for mill sheet request to material manufacturer company.
Thread length of hex bolt half-thread
As you know, there are two types of hex bolts: full thread and half thread. The half screw is actually a calculation formula that tells you the length of a half screw no matter what length it is.
For half-thread bolt, there is calculation formula to check the thread length regardless of their length.
The calculation formula is
(Nominal diameter x 2) + 6
If the length under the bolt neck is equal to 130L or more,
Formula will be (Nominal diameter x 2) + 12
*Note: For 220L or more, Formular will be (Nominal diameter x 2) + 25
*Note 2: Each company may have their own standards
For example, in the case of M16x80 >> (16 x2) + 6 = 38, so you can see that the screw length of M16x80 is approximately 38mm.
If you know this, you will know which one should we select to our application, and if you work at a screw shop, when a customer asks you to tell them the length of a half-screw, you don't have to look at the catalog, you can answer this back to customer right away.
Height of hexagon nuts
There is one more thing that I would like everyone to remember. That's the height of the hex nut.
There are 1, 2, and 3 types of hex nuts, and the height can be determined by the thread diameter of each type.
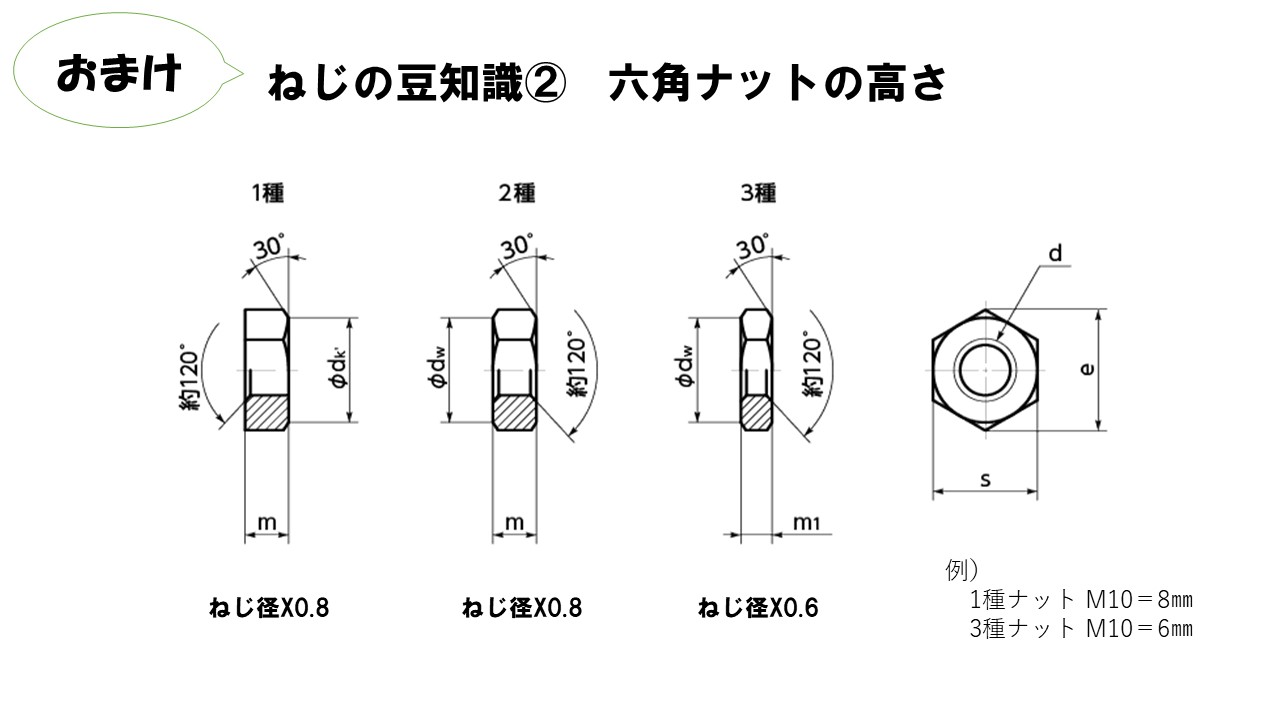
For example, in the case of type-1 and type-2, the height is the same, so you can find it by multiplying by 0.8.
For example ; M10 hex nut Type-1 or Type-2, M10 = 10x0.8
Then the nut height is approximately = 8mm
In the case of Type-3, it will be x0.6.
For example; M10, M10=10x0.6
Then the nut height is approximately = 6mm
Thank you for reading this content! I will write again next time, please stay tune!



